Generating Excel output from PL/SQL is a common requirement. But, there is no built-in function/API in Oracle Database which you can use to generate it. In this article, I will show how to get excel from PL SQL using dbms_output.put_line, utl_file available in Oracle.
Note:- The file generated using some of these methods is not actual excel, but yes, you can open/edit/save them in Microsoft Excel.
1. Generate CSV or Pipe Delimited file using PL/SQL
CSV (Comma Separated Values) or Pipe delimited files are flat files where a character like Comma, PIPE, or any other character separates words. Most of the spreadsheets can directly open these files.
So you can use dbms_ouput.put_line or utl_file API to create a delimited file that excel can easily open.
SET FEEDBACK OFF
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON
SPOOL employee_list.dat
DECLARE
CURSOR employee
IS
SELECT
first_name ,
last_name,
email,
phone_number,
hire_Date
FROM
employees;
BEGIN
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line('First Name|Last Name|Email|Phone Number|Hire Date');
FOR rec_employee IN employee
LOOP
dbms_output.put_line(rec_employee.first_name||'|'||rec_employee.last_name ||'|'||
rec_employee.email || '|' || rec_employee.phone_number||'|' ||
rec_employee.hire_Date);
END LOOP;
END;
/
SPOOL OFF;
2. Excel file using as_xlsx PL/SQL Package
You can use as_xlsx package created by Anton Scheffer to generate an Excel file from the database. Get the source code from here, compile in the database, and the run below query to generate the file.
begin as_xlsx.query2sheet( 'select * from dba_objects where rownum <100' ); as_xlsx.save( 'TEMP_DIR', 'dba_objects.xlsx' ); end;
Here, TEMP_DIR is DBA_DIRECTORY.
3. Generate XML excel spreadsheet 2003 standard
This is a bit lengthy method, it actually creates the structure of excel using XML. The problem with this method is file size is big, as it generates tags for each cell and row.
Let’s design a program for this. This is the XML excel spreadsheet 2003 standard.
SET FEEDBACK OFF
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON SIZE 100000
SPOOL employee_data.xls
DECLARE
l_header VARCHAR2(100);
CURSOR employee
IS
SELECT
'<Row>' start_row ,
'<Cell><Data ss:Type="String">' || first_name || '</Data></Cell>' first_name,
'<Cell><Data ss:Type="String">' ||last_name || '</Data></Cell>' last_name,
'<Cell><Data ss:Type="String">' ||email || '</Data></Cell>' email ,
'</Row>' end_row
FROM
employees;
BEGIN
dbms_output.put_line('
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?mso-application progid="Excel.Sheet"?>
<Workbook xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:spreadsheet" xmlns:o="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:office" xmlns:x="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:excel" xmlns:ss="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:spreadsheet" xmlns:html="http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-html40">
<DocumentProperties xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:office">
<LastAuthor>ATT</LastAuthor>
<Created>2016-10-10T18:17:29Z</Created>
<LastSaved>2016-10-10T18:13:54Z</LastSaved>
<Version>11.5606</Version>
</DocumentProperties>
<ExcelWorkbook xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:excel">
<WindowHeight>7005</WindowHeight>
<WindowWidth>10005</WindowWidth>
<WindowTopX>105</WindowTopX>
<WindowTopY>105</WindowTopY>
<ProtectStructure>False</ProtectStructure>
<ProtectWindows>False</ProtectWindows>
</ExcelWorkbook>
<Styles>
<Style ss:ID="Default" ss:Name="Normal">
<Alignment ss:Vertical="Bottom"/>
<Borders/>
<Font ss:Color="#000000"/>
<Interior/>
<NumberFormat/>
<Protection/>
</Style>
<Style ss:ID="s21">
<NumberFormat/>
</Style>
<Style ss:ID="s24">
<Alignment ss:Vertical="Bottom" ss:WrapText="1"/>
</Style>
<Style ss:ID="s26">
<Alignment ss:Horizontal="Center" ss:Vertical="Bottom" ss:WrapText="1"/>
<Font x:Family="Swiss" ss:Color="#000000" ss:Bold="1"/>
<Interior ss:Color="#FFFF00" ss:Pattern="Solid"/>
</Style>
</Styles>');
dbms_output.put_line('<Worksheet ss:Name="Employee">');
dbms_output.put_line('
<Table ss:ExpandedColumnCount="2000" ss:ExpandedRowCount="64000" x:FullColumns="1" x:FullRows="1">');
dbms_output.put_line('<Column ss:AutoFitWidth="0" ss:Width="56.25" />
<Column ss:AutoFitWidth="0" ss:Width="50.00" />
<Column ss:AutoFitWidth="0" ss:Width="100.00" />');
dbms_output.put_line('<Row ss:AutoFitHeight="0" ss:Height="24.75" ss:StyleID="s24">
<Cell ss:StyleID="s26"><Data ss:Type="String">Fist Name</Data></Cell>
<Cell ss:StyleID="s26"><Data ss:Type="String">Last Name</Data></Cell>
<Cell ss:StyleID="s26"><Data ss:Type="String">Email</Data></Cell>
</Row>');
FOR rec_employee IN employee
LOOP
dbms_output.put_line(rec_employee.start_row);
dbms_output.put_line(rec_employee.first_name);
dbms_output.put_line(rec_employee.last_name);
dbms_output.put_line(rec_employee.email);
dbms_output.put_line(rec_employee.end_row);
END LOOP;
dbms_output.put_line( '</Table>
<WorksheetOptions xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:excel">
<PageSetup>
<Header x:Margin="0"/>
<Footer x:Margin="0"/>
</PageSetup>
<NoSummaryColumnsRightDetail/>
<Print>
<ValidPrinterInfo/>
<HorizontalResolution>600</HorizontalResolution>
<VerticalResolution>600</VerticalResolution>
</Print>
<PageBreakZoom>100</PageBreakZoom>
<Selected/>
<LeftColumnVisible>41</LeftColumnVisible>
<Panes>
<Pane>
<Number>3</Number>
<ActiveCol>48</ActiveCol>
<RangeSelection>C49</RangeSelection>
</Pane>
</Panes>
<ProtectObjects>False</ProtectObjects>
<ProtectScenarios>False</ProtectScenarios>
</WorksheetOptions>
</Worksheet>' );
dbms_output.put_line('</Workbook>');
END;
/
SPOOL OFF
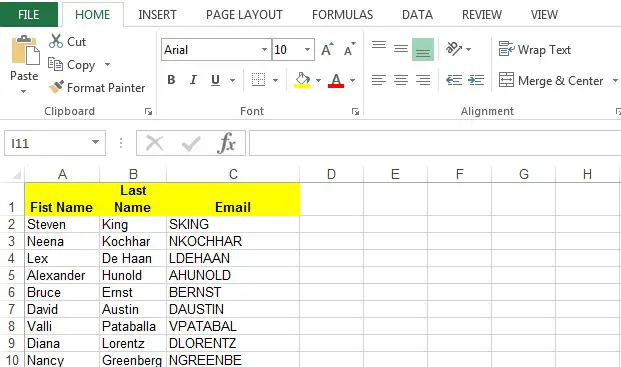
Final Output
This is the final output in excel format.
Summary
Oracle database does not provide a built-in method to generate an Excel file, but you can use the method explained in this article to generate a file that excels can understand and opens.
Please let me know if you found this useful or I am missing any other method.